What is a Circular Economy? Understanding the Sustainable Cycle
If you’ve ever wondered about the term “circular economy,” you’re not alone. The concept can seem daunting at first, but breaking it down into smaller pieces reveals its significance and potential impact. Let’s delve into what exactly entails and why it’s becoming increasingly crucial in today’s world.
Explanation
At its core, the term “circular” refers to the process of utilizing a product or resource in a way that minimizes waste and maximizes its lifecycle. Rather than following a linear path of consumption and disposal, it promotes practices such as recycling, reusing, repairing, and sharing, thereby closing the loop on resource utilization. This approach not only conserves valuable resources but also reduces environmental footprint by minimizing waste generation.
The Importance
The significance extends beyond environmental conservation. By adopting circular practices, companies can optimize their financial resources by prolonging the lifespan of products and minimizing the need for new resource investments. Moreover, it fosters resilience within local economies by reallocating resources to where they are most needed, thus promoting sustainable growth and development.
Components
Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
The mantra of “reduce, reuse, recycle” lies at the heart of the principles. By prioritizing waste reduction, encouraging reuse of products, and promoting recycling initiatives, CE aims to minimize resource depletion and environmental degradation.
Extended Product Lifecycles
Central is the concept of extending product lifecycles through innovative design, repair, and refurbishment. By designing products with longevity in mind and providing avenues for repair and maintenance, companies can maximize the utility of their products while minimizing waste generation.
Benefits
Environmental Benefits
CE practices offer numerous environmental benefits, including reduced resource consumption, minimized waste generation, and lower greenhouse gas emissions. By promoting sustainable resource management, it contributes to biodiversity conservation and mitigates environmental degradation.
Economic Benefits
In addition to environmental advantages it presents significant economic benefits for businesses and society as a whole. By optimizing resource utilization and reducing waste disposal costs, companies can enhance their profitability and competitiveness. Moreover, fostering job creation and stimulating economic growth through innovative solutions and new business opportunities.
Social Benefits
Initiatives also yield social benefits by promoting inclusivity, resilience, and community engagement. By prioritizing resource efficiency and equitable resource distribution, circular economy contributes to poverty alleviation, social cohesion, and improved quality of life for communities worldwide.
Challenges and Barriers
Despite its numerous benefits, the widespread adoption faces several challenges and barriers.
Lack of Awareness
One of the primary challenges hindering the uptake of circular economy practices is the lack of awareness and understanding among stakeholders. Addressing this challenge requires robust education and awareness campaigns to highlight the benefits and promote behavior change among consumers and businesses.
Infrastructure Challenges
Implementing initiatives often requires significant investments in infrastructure and technology. Inadequate infrastructure, particularly in developing countries, poses a barrier to the effective implementation of circular economy practices. Addressing infrastructure gaps and building capacity are essential steps towards advancing circular economy objectives globally.
Policy and Regulation
The absence of supportive policy frameworks and regulatory mechanisms presents a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of circular economy practices. Governments and policymakers play a crucial role in creating an enabling environment by implementing incentives, regulations, and standards that promote resource efficiency and sustainable consumption.
Examples of Initiatives of Circular Economy
Case Study 1: Fashion Industry
The fashion industry is increasingly embracing circular economy principles to address sustainability challenges such as textile waste and environmental degradation. Initiatives such as clothing rental platforms, textile recycling programs, and sustainable fashion design are transforming the industry’s linear model into a circular one, thereby reducing its environmental footprint and promoting resource efficiency.
Case Study 2: Food Industry
In the food industry, circular economy initiatives focus on minimizing food waste, optimizing resource use, and promoting sustainable production and consumption practices. From farm to fork, circular economy principles are applied through measures such as surplus food redistribution, organic waste recycling, and sustainable packaging solutions, leading to a more resilient and sustainable food system.
Implementing Circular Economy Practices
Achieving the transition requires collective action and collaboration across sectors and stakeholders. Key strategies for implementing practices include:
-
Collaboration and Partnerships: Fostering collaboration among businesses, governments, NGOs, and communities is essential for driving systemic change and scaling up circular economy initiatives.
-
Innovation and Technology: Leveraging innovation and technology is critical for developing circular economy solutions that are scalable, efficient, and cost-effective. From advanced recycling technologies to sustainable materials and design innovations, technology plays a pivotal role in accelerating the transition to a circular economy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the concept of circular economy offers a holistic and sustainable approach to resource management and economic development. By prioritizing waste reduction, resource efficiency, and innovation, it enables businesses and societies to thrive within planetary boundaries while promoting environmental stewardship and social equity. However, overcoming challenges such as lack of awareness, infrastructure gaps, and policy barriers requires concerted efforts and collective action. By embracing circular economy principles and fostering collaboration, we can create a more resilient, equitable, and sustainable future for generations to come.
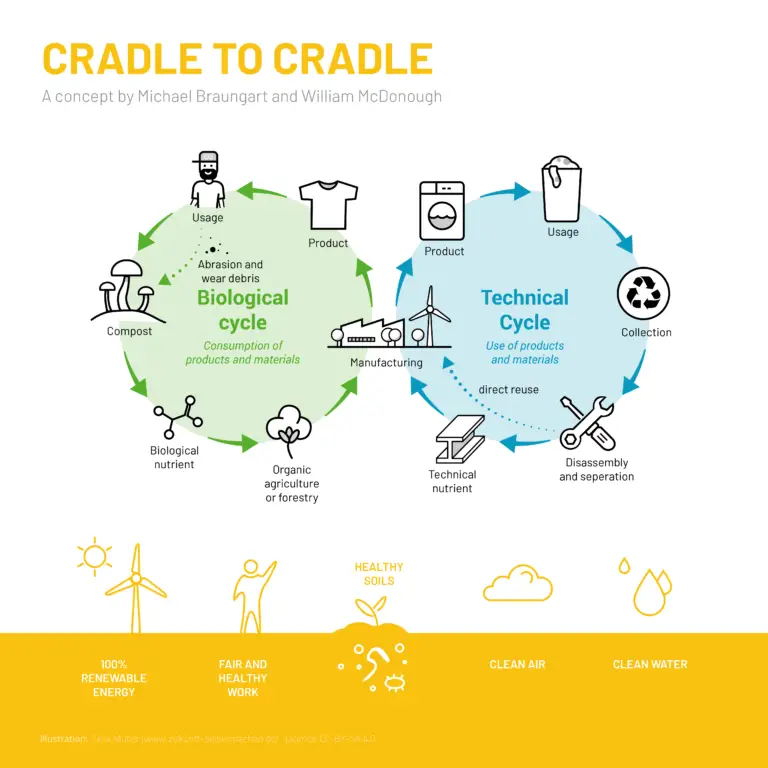
Can I have examples?
Sure! We are one! mellow designs’ works with circularity and sustainable business growth at our core, to help YOU go from a linear to a circular economy in your own company.
So, you probably have a better idea now about what circular economy is. If you still have questions, reach out to us! We are experts in this area and would love to make you one as well.
Latest Articles


building better with adaptable partition walls
